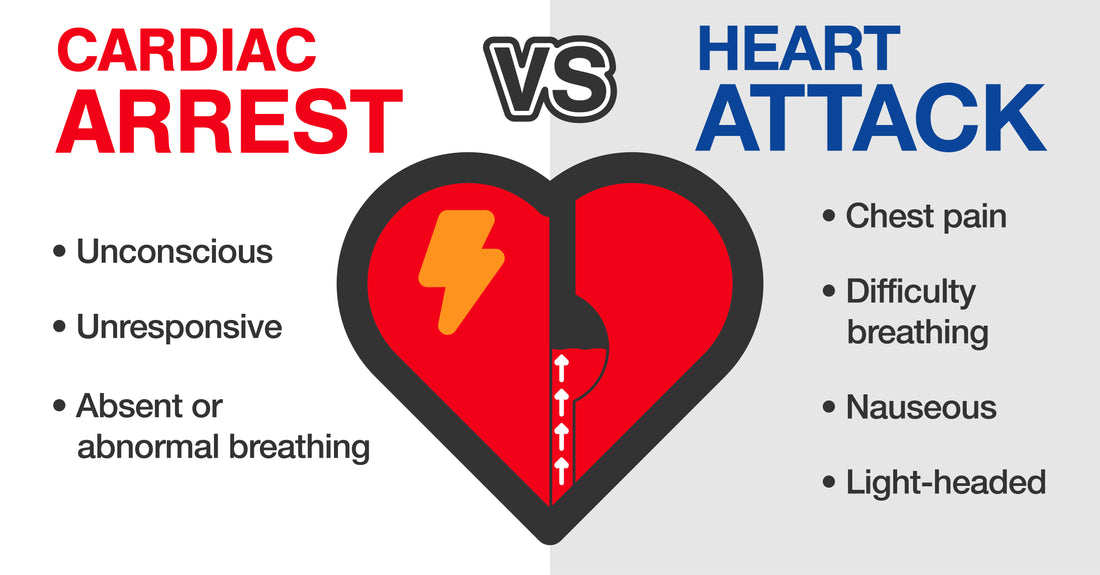
When it comes to heart health, it's important to understand the difference between sudden cardiac arrest and a heart attack. While these terms are often used interchangeably, they are actually two distinct medical events with different causes and outcomes.
What is a Heart Attack?
A heart attack, also known as a myocardial infarction¹, occurs when there is a blockage in one or more of the coronary arteries² that supply blood to the heart muscle. This blockage is usually caused by a build up of fatty deposits called plaque. When the blood flow to a part of the heart is blocked, that part of the heart muscle becomes damaged or dies.
What are the Symptoms of a Heart Attack?
The symptoms of a heart attack can vary from person to person, but common signs include:
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Shortness of breath
- Feeling lightheaded or dizzy
- Nausea or vomiting
- Pain or discomfort in the jaw, neck, or back
What is Sudden Cardiac Arrest?
Sudden cardiac arrest, on the other hand, is a sudden and unexpected loss of heart function. It occurs when the heart's electrical system malfunctions, causing the heart to stop beating. This can happen due to a variety of reasons, including an abnormal heart rhythm called ventricular fibrillation³.
What are the Symptoms of Sudden Cardiac Arrest?
Unlike a heart attack, sudden cardiac arrest often occurs without warning and the person may lose consciousness immediately. Other symptoms may include:
- No pulse or breathing
- Sudden collapse
- Loss of responsiveness
What is the Difference?
The main difference between sudden cardiac arrest and a heart attack lies in their underlying causes. A heart attack is caused by a blockage in the coronary arteries, while sudden cardiac arrest is caused by a malfunction in the heart's electrical system. Additionally, a heart attack can lead to sudden cardiac arrest if it is not treated promptly.
What to Do in an Emergency?
If someone is experiencing symptoms of a heart attack or sudden cardiac arrest, it is crucial to seek immediate medical attention. Call emergency services and perform CPR if necessary. Learn how to here⁴. Early intervention can greatly increase the chances of survival and minimize long-term damage to the heart.
Conclusion
While sudden cardiac arrest and a heart attack are both serious medical events related to the heart, they have different causes and require different treatments. Understanding the difference between the two can help individuals recognize the symptoms and take appropriate action in an emergency situation. Remember, when it comes to matters of the heart, knowledge is power.

References:
1. Myocardial Infarction | National Library of Medicine
2. Anatomy and Function of the Coronary Arteries | Johns Hopkins Medicine